The UK’s largest independent producer of official statistics has published a nationwide distance and travel time analysis that shows access to local amenities in England and Wales

Britain’s Office for National Statistics (ONS) has been studying public access to amenities across the nation, Including an investigation published in early 2024. analysing access to sports facilities, supermarkets and museums.
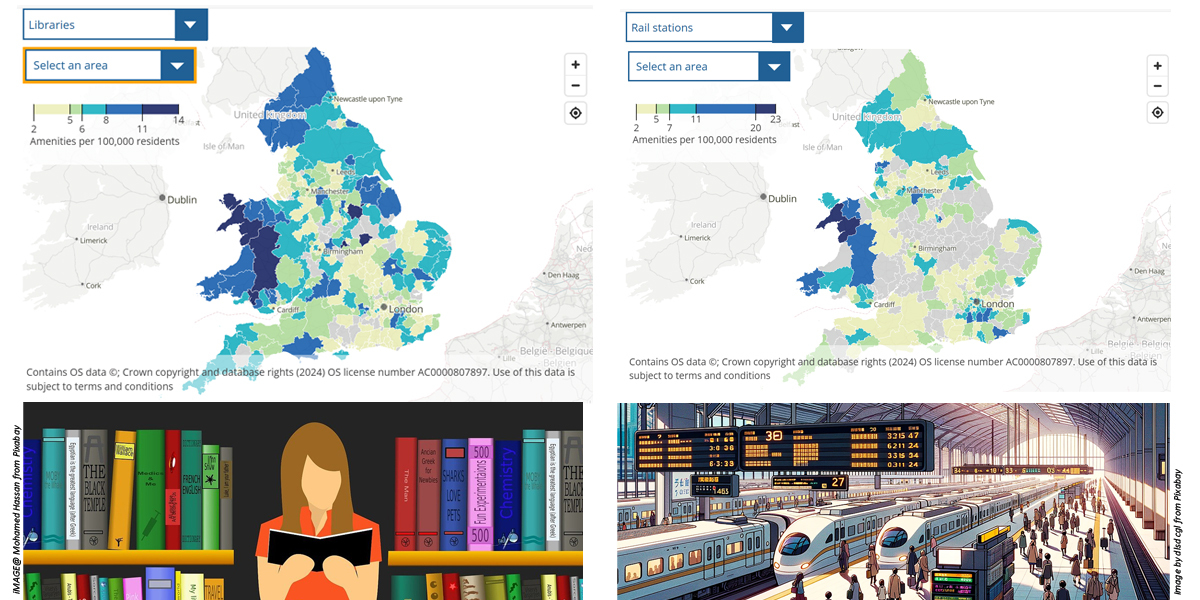
ONS has since expanded the range of amenities to describe how provision varies between and within local areas. The Access to amenities in local areas: October 2024 publication includes an interactive map covering local provision of ATMs and cash points, dental practices, GP surgeries, pharmacies, post offices, and more.
ONS recognised that the number of amenities available to residents did not factor in how far or time-consuming they may be to reach - an important consideration for amenity access.
For this reason, it turned to the national mapping agency, Ordnance Survey (OS), for location expertise and insight, to analyse travel times for two key amenities: railway stations, and libraries. Analysing travel time meant identifying the nearest railway station and libraries for inhabited 100m grid squares.
OS Senior Data Scientist Mark Freeman identified 100m squares containing residential properties across Great Britain. For libraries and railway stations, Mark used OS NGD Land Use data, which identified specific building types, in addition to respective access points.
The analysis measured distance and time needed to reach destinations, either driving or walking. The roads and paths followed were taken from the OS Multi-modal Routing Network (MRN). The purpose of the analysis was to try to ascertain the shortest travel time between each grid and a library/rail station, not necessarily the shortest distance. Walking routes would include height and slope of pathways, trying to avoid hills, while driving routes would factor in one-way roads and speed restrictions.
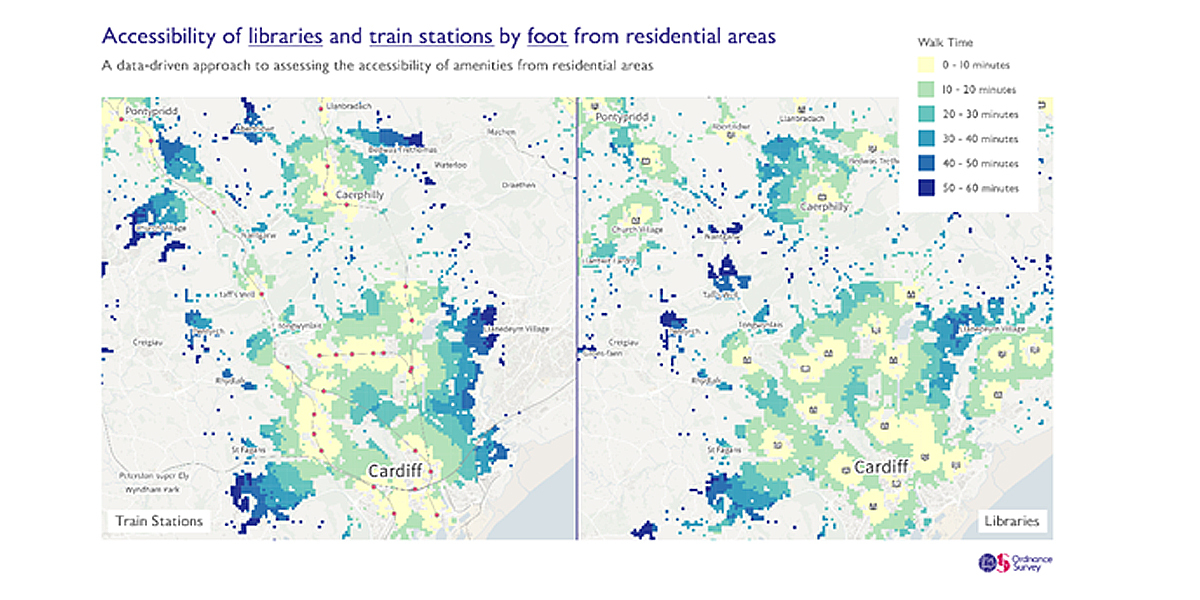
Each grid square was assigned a time to its nearest amenity and the name of that amenity. ONS could then use the travel times – from grid square to nearest amenity – to estimate the proportion of the population within travel time bands for larger geographic areas. ONS then factored these results, along with other data such as population, into their analysis to consider which local areas had good access to amenities.
Key findings
ONS has shared some interesting stats from their analysis:
• More than half (57%) of the population of England and Wales live within a 30-minute walk of a railway station.
• Approximately 78% of the population of England and Wales are within a 30-minute walk of a public library, but this is higher in urban local authorities than in rural local authorities.
Future applications
ONS has successfully delivered two key studies – analysis of access to sports facilities, and now libraries and Rail stations. The methodology can be applied to any number of other projects across the public sector. ONS could expand its analysis, studying the same distance/time routes between homes and other important amenities such as hospitals, schools, and so on. It could unlock insight and help identify properties with minimal-to-no amenities, essential in planning for the accessibility of public services to residents.
It could also prove beneficial in the analysis and planning of the ‘20-minute neighbourhood’ concept – an idea that investigates whether people can achieve their essential needs within a 20-minute walk of their home.

In the private sector, retail organisations could analyse access to premises, and identify optimum locations to build new branches that enables them to better serve communities.
OS is currently considering how the process could be improved further to make it faster and more efficient for public sector organisations to generate their own distance and travel time insights, on a large scale.
John Kimmance, Chief Customer Officer at OS, said: “This is a great example of how OS expertise in the development of geospatial insights can be applied to a huge variety of different projects. This can help public sector organisations at a national and local level with valuable insights which enable the most effective delivery of services to the general public.”
OS provides its data and services to the emergency services and wider public sector organisations through the Public Sector Geospatial Agreement (PSGA). The PSGA is a contract between the government and OS for the provision of geospatial data across multiple themes, including buildings, transport, structures, addressing and land. The contract delivers key data to public sector members for use in everyday settings to support provision of critical services to the public.
All OS data can be accessed via the OS Data Hub.
Story Source: Ordnance Survey
Subscribe to our newsletter
Stay updated on the latest technology, innovation product arrivals and exciting offers to your inbox.
Newsletter

