Researchers at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California have mapped scorching pavement in Phoenix, Arizona, where contact with skin—from a fall, for example—can cause serious burns

Data for the visualization of the Phoenix area—the fifth most populous city in the United States—was collected at 1:02 p.m. local time on June 19, 2024, by a NASA instrument aboard the International Space Station.
Called ECOSTRESS (short for the Ecosystem Spaceborne Thermal Radiometer Experiment on Space Station), the instrument measures thermal infrared emissions from Earth's surface.
The image (below) shows how miles of asphalt and concrete surfaces (colored in yellow, red, and purple, based on temperature) trap heat. The surfaces registered at least 120°F (49°C) to the touch—hot enough to cause contact burns in minutes to seconds.
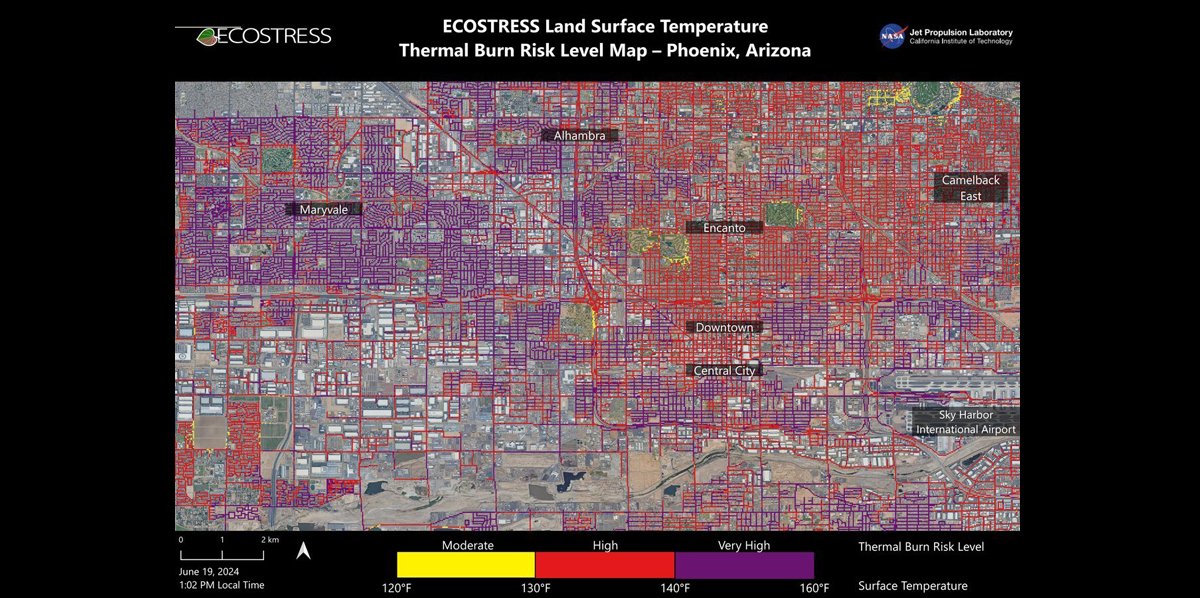
The image also shows cooling effects of green spaces in communities like Encanto and Camelback East, in contrast to the hotter surface temperatures seen in Maryvale and Central City, where there are fewer parks and trees.
"We create these maps to be intuitive to users and help make data more accessible to the public and citizens scientists," said Glynn Hulley, a JPL climate researcher. "We see them as a vital tool for planning effective heat interventions, such as tree planting, that can cool down the hottest roads and sidewalks."
Homing in on heat
At the lower right of the image is Phoenix's Sky Harbor International Airport, where ECOSTRESS recorded some of the hottest land surface temperatures within the city—about 140°F (60°C). The air temperature on June 19 at the airport reached 106°F (43°C).
Air temperature, which is measured out of direct sunlight, can differ significantly from the temperature at the land surface. Streets are often the hottest surfaces of the built environment due to dark asphalt paving that absorbs more sunlight than lighter-colored surfaces; asphalt absorbs up to 95% of solar radiation. These types of surfaces can easily be 40°F to 60°F (22°C to 33°C) hotter than the air temperature on a very hot day.
Launched to the International Space Station in 2018, ECOSTRESS has as its primary mission the identification of plants' thresholds for water use and water stress, giving insight into their ability to adapt to a warming climate. But the instrument is also useful for documenting other heat-related phenomena, like patterns of heat absorption and retention.
To produce the image of Phoenix, scientists used a machine learning algorithm that incorporates data from additional satellites: NASA/USGS Landsat and Sentinel-2. The combined measurements were used to "sharpen" the surface temperatures to a resolution of 100 feet (30 meters) by 100 feet (30 meters).
Source: NASA
Subscribe to our newsletter
Stay updated on the latest technology, innovation product arrivals and exciting offers to your inbox.
Newsletter

